[Paper Reivew] Visual Autoregressive Modeling: Scalable Image Generation via Next-Scale Prediction
Flow matching의 comprehensive and self-contained reviewd 입니다.
NeurIPS 2024 Best Paper, Oral [Paper] [Github]
Keyu Tian, Yi Jiang, Zehuan Yuan, Bingyue Peng, Liwei Wang
Peking University | Bytedance Inc
3 Apr 2024
TL;DR
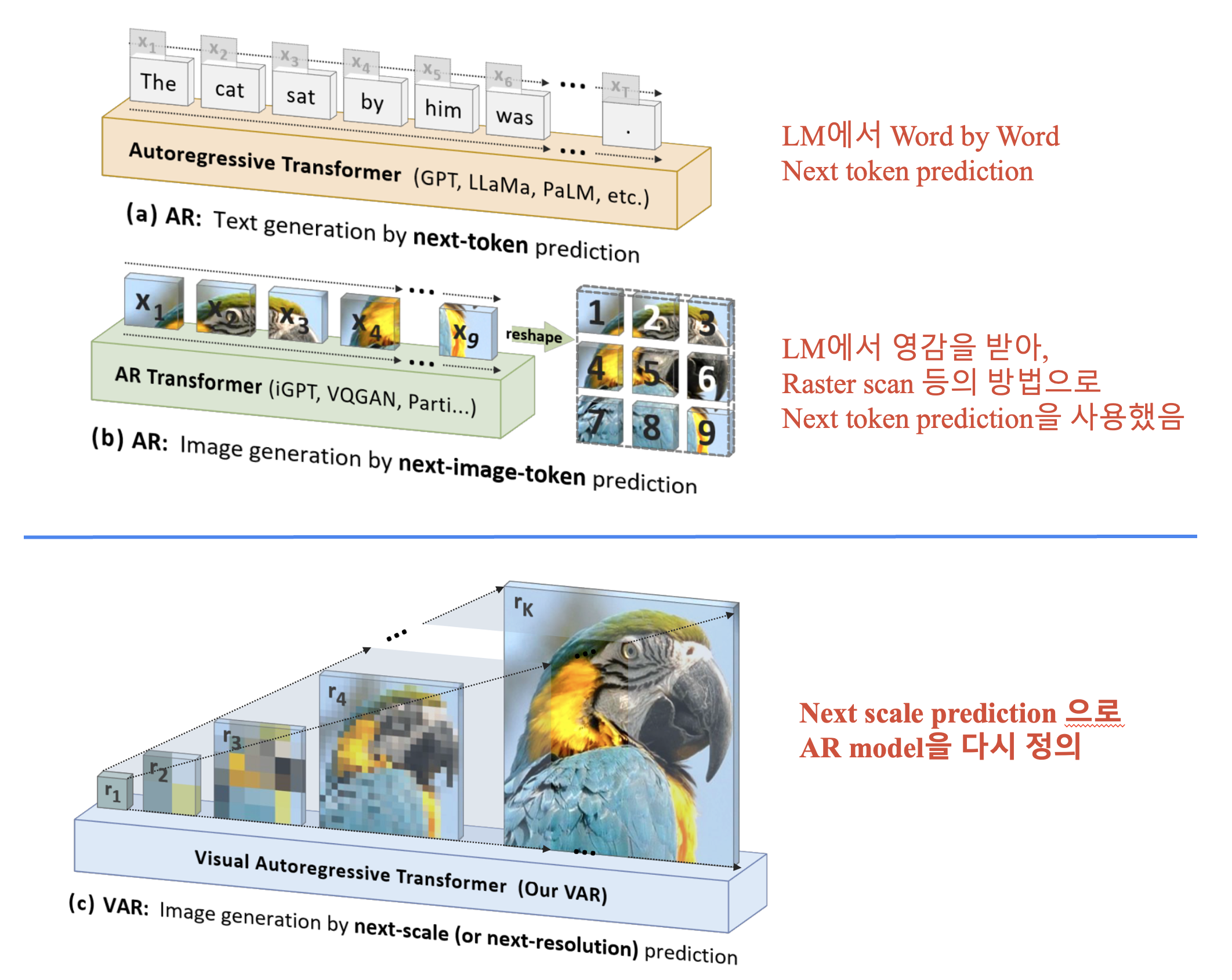
VAR은 AR 기반 모델로, 기존 Next-token prediction에서 Next-scale prediction으로 AR 모델을 새롭게 정의합니다.
- AR 기반 LLM의 특성인 Scalability, Generalizabilty의 특성을 Vision 모델로 가져옴.
- Diffusion model에 비해 훨씬 더 적은 시간으로, 처음으로 ImageNet 256x256에서 FID 성능을 능가
1. Introduction
LLM의 기반인 Autoregressive (AR) model은 2가지 특성을 갖습니다.
- Scalability : Large model로 갈수록 성능이 높아짐.
- Generalizabilty : Zero-shot, few-shot task 적용 가능.
이런 장점을 Vision 분야로 가져오려는 연구들, VQGAN, DALL-E 같은 모델들은 AR모델의 Potential을 보여주었습니다. 이런 모델들은 visual tokenizer를 이용해서 연속적인 이미지를 2D token으로 나누고, 이를 1D sequence로 flatten합니다. 하지만 이런 모델들은 제대로 성능이 나오지 않으며, scaling law가 되지 않는다는 문제가 있다고합니다.
이에 저자들은 data를 ordering하는 방식에 대해 다시 고려합니다. 인간들은 일반적으로 hierachical 방식으로 이미지를 인식, 생성하는 것처럼, multi-scale, coarse-to-fine 방식으로 next-scale prediction 방식을 제안합니다.
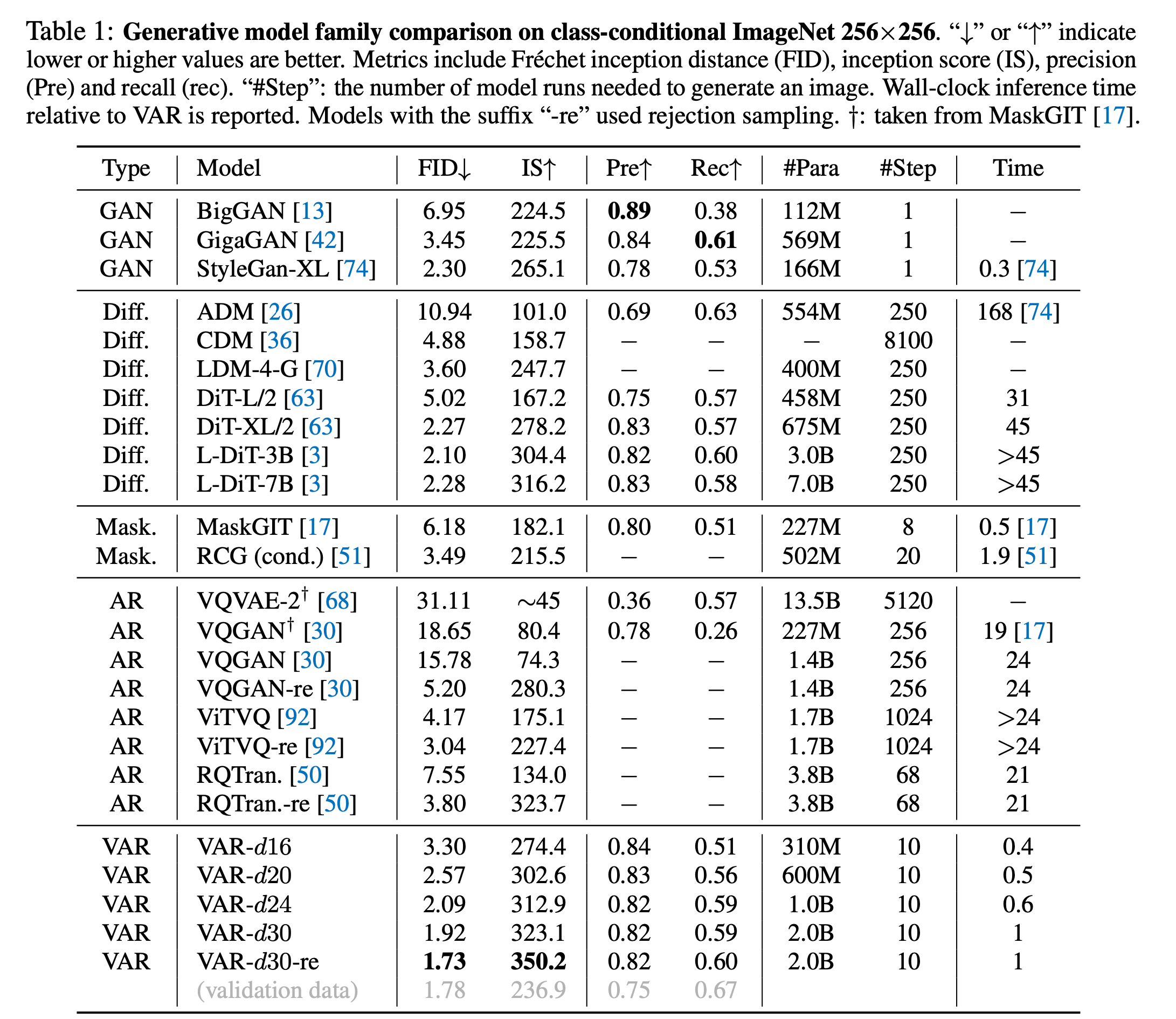
저자들의 방법론 Visual AutoRegressive (VAR)은 ImageNet 256x256에서 FID 1.73을 달성하며, 처음으로 Diffusion 기반 방법론을 능가하는 성능을 보여주었다고 합니다.
저자들의 주요 contribution은 다음과 같습니다.
- Next-scale prediction을 사용하는 VAR 방식을 제안합니다.
- VAR은 Scaling Law, zero-shot generalization potential의 특성을 갖습니다.
- 처음으로 AR 방식으로 Diffusion 기반 방식의 성능을 능가했습니다.
2. Related Work
2.1. Properties of large autoregressive language models
Scaling laws : AR 모델의 주요 특성인 scaling laws는 model, dataset, computation 등의 scale을 키우면, 모델의 성능이 올라가는 것을 의미합니다. Scaling laws는 작은 모델로 더 큰 모델의 성능을 예측할 수 있다는 장점이 있습니다.
Zero-shot generalization : 학습되지 않은 task를 수행하는 능력을 Zero-shot generalization라고 합니다. Vision에서도 zero-shot and in-context learning 능력을 가진 foundation model을 만들려는 CLIP, SAM, Dinov2 같은 연구들이 있습니다.
3. Method
3.1. Preliminary: autoregressive modeling via next-token prediction
Unidirectional token dependency assumption은 다음과 같은 식으로 표현 가능합니다. \(p(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_T) = \prod_{t=1}^{T} p(x_t \mid x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_{t-1}).\) 이는 Next-token prediction이라하며, 새로운 sequence를 생성하도록 \(p_\theta\)를 학습합니다.
이미지는 기본적으로 연속적인 2D signal입니다. AR 모델에 image를 적용하기 위해서는 Tokenization, 1D Ordering 과정이 필요합니다.
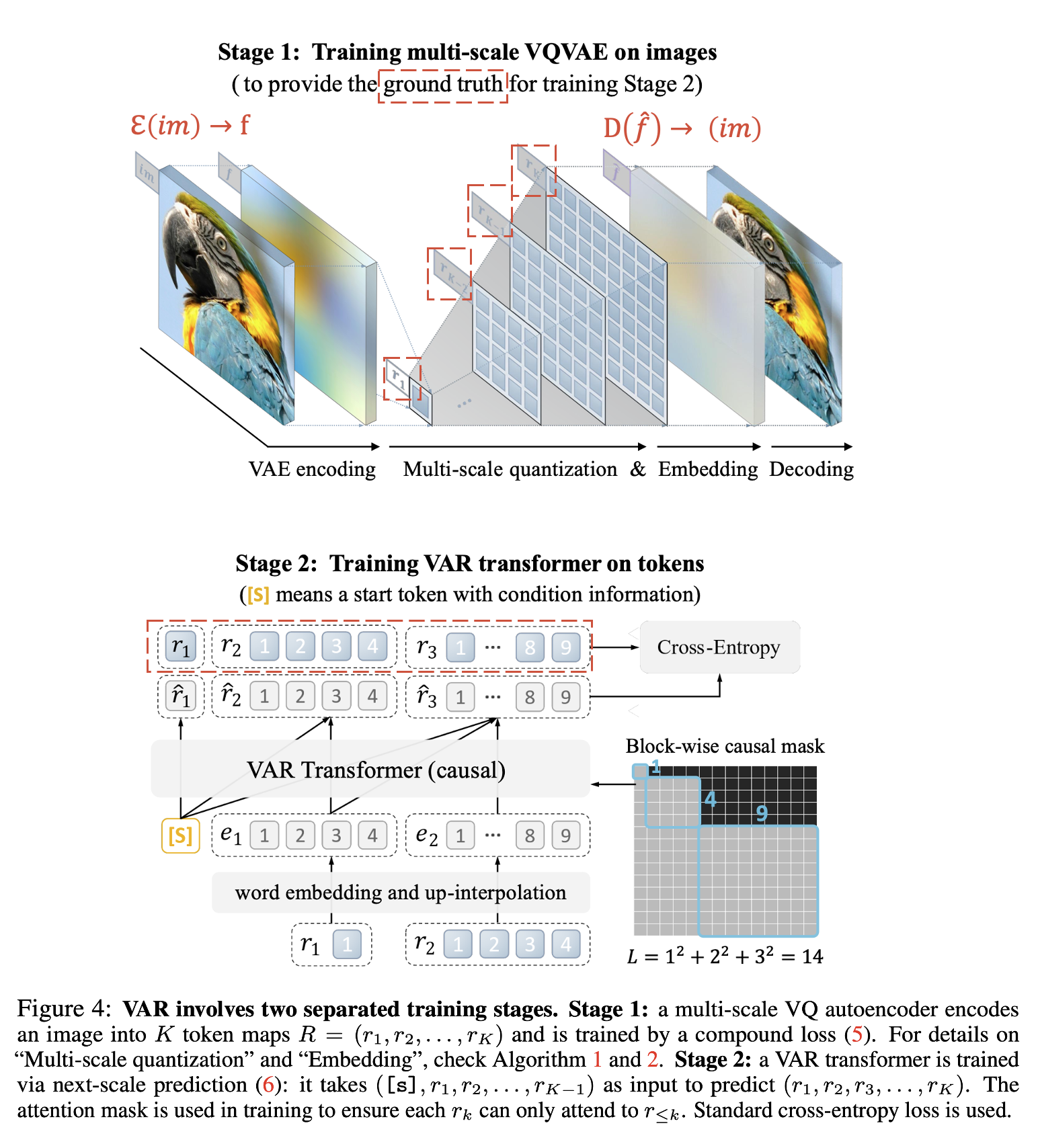
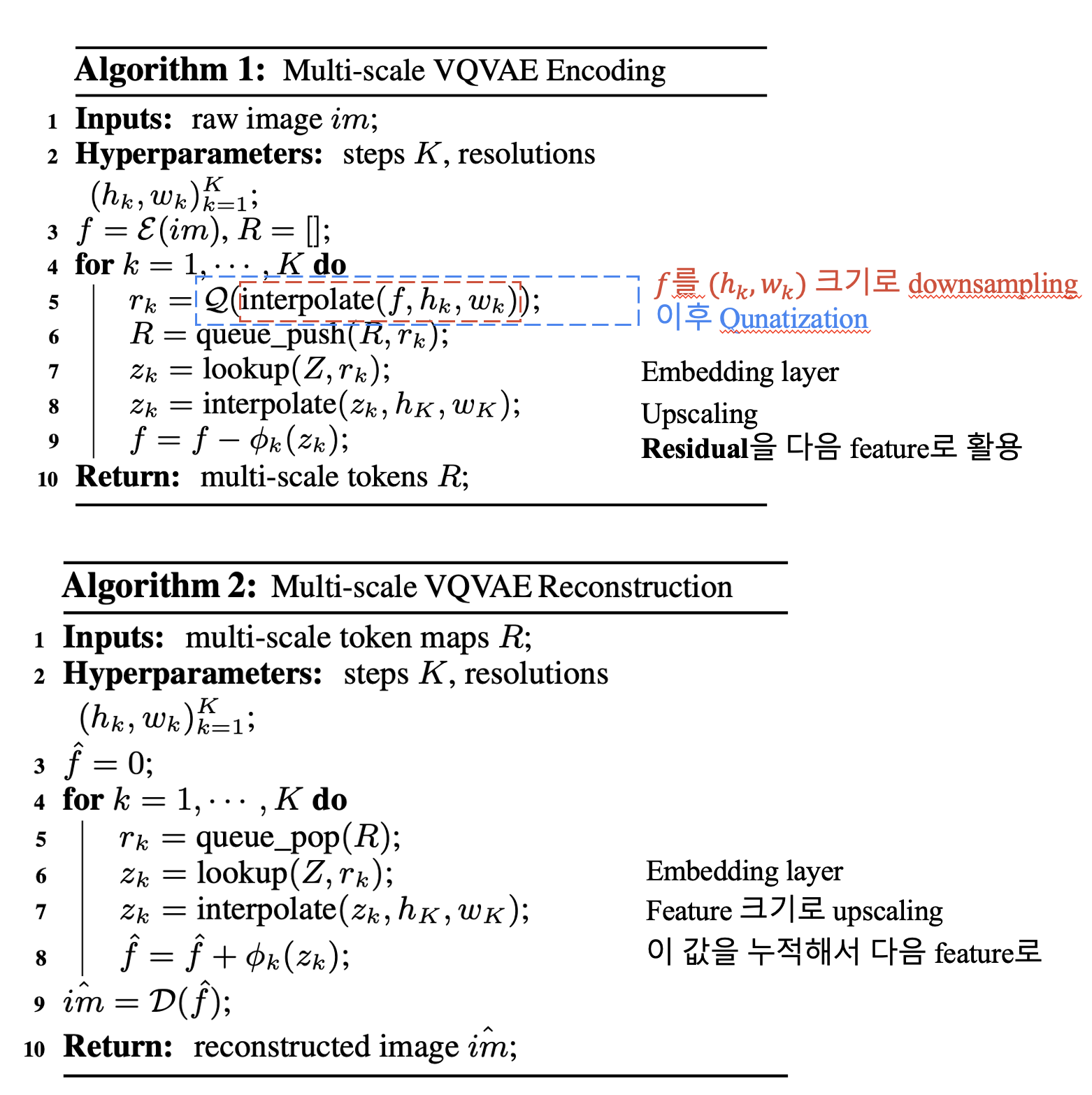
- Tokenization : 이미지를 discrete token으로 나누는 과정, Quantized autoencoder을 이용해, image feature map \(f \in \mathbb R^{h \times w \times C }\)을 discrete token \(q \in [V]^{h\times w}\)로 변환합니다. \(f = \mathcal{E}(im), \quad q = \mathcal{Q}(f),\)
이때 quantizer 는 일반적으로 학습 가능한 codebook \(Z \in \mathbb R^{V \times C}\)를 포함하는데, quantization 과정은 feature vector를 가장 가까운 code index에 mapping하는 과정입니다.
\[q^{(i,j)} = \left( \arg\min_{v \in [V]} \lVert \text{lookup}(Z, v) - f^{(i,j)} \rVert_2 \right) \in [V],\]\(\text{lookup}(Z, v)\)는 codebook \(Z\)에서 \(v\)-th vector를 취하는 것입니다. Qunatized AE를 학습하기 위해서는 \(Z\)는 모든 \(\hat f\)를 얻기 위해 모든 \(q^{(i,j)}\)를 확인해야 합니다.
이후 새로운 이미지 \(\hat{im}\)은 decoder \(\mathcal D\)에 의해 recon 됩니다.
\(\hat{f} = \text{lookup}(Z, q), \quad \hat{im} = \mathcal{D}(\hat{f}),\) \(\mathcal{L} = \lVert im - \hat{im} \rVert_2 + \lVert f - \hat{f} \rVert_2 + \lambda_\mathcal{P} \mathcal{L}_\mathcal{P}(\hat{im}) + \lambda_\mathcal{G} \mathcal{L}_\mathcal{G}(\hat{im}),\)
- Ordering : Unidirectional 모델링을 위해 token을 1D로 배치해야 합니다. 이때 aster scan, spiral, z-curve order 방식등이 있습니다만… 이렇게 Flatten하고, next-token prediction하는 모델들은 모두 Unidirectional 하지 않다고 합니다.
- Mathematical premise violation : Quantized AE에서 encoder는 모든 feature vector에 대해 inter-dependent한 이미지 feature를 생성합니다. 따라서 이를 flatten 해도 bidirectional한 특성이 남아있다고 합니다.
- zero-shot generalization 부족 : Unidirectional의 특성상 이미지에서 일반화가 잘 안된다고 합니다. ( 기존 방식으로는 아래쪽 이미지를 보고 위쪽 이미지 맞추기 안됨)
- Structural degradation : Flatten하는 과정은 근본적으로 spatial locality를 방해한다고 합니다. Language 모델과 다르게 image는 주변 여러 픽셀의 영향을 받기 때문입니다.
- Inefficiency : 기존 self-attention transformer는 \(\mathcal O(n^2)\)의 AR step과, \(\mathcal O(n^6)\) computational cost가 들며 이는 비효율적이라 합니다.
3.2. Visual autoregressive modeling via next-scale prediction
Reformulation
저자들은 기존 next-token prediction에서 next-scale prediction으로 AR 모델을 새롭게 정의합니다. AR의 unit을 single token이 아니라, entire token map, \(r_k\)로 바꾸는 것입니다.
\[p(r_1, r_2, \ldots, r_K) = \prod_{k=1}^{K} p(r_k \mid r_1, r_2, \ldots, r_{k-1}).\]Discussion
VAR은 앞서 언급한 문제들을 해결합니다.
- mathematical premise 만족 : \(r_k\)는 prefix에만 영향을 받으며, coarse-to-fine 방식으로 이미지 생성.
- spatial locality 보존: flattening 없고, 각 \(r_k\)는 병렬적으로 생성되므로 fully correlated.
- Efficiency : \(\mathcal O(n^4)\) computational cost로 효율적인 이미지 생성.
Tokenization
저자들은 이미지를 \(K\)개의 multi scale token로 encoding하기 위해서 새로운 multi-scale quantization AE를 제안합니다.
VQGAN과 동일한 구조를 가져가지만, multi-scale quantization layer를 수정해서 residual design을 택해 성능을 높였다고 합니다.
5. Empirical Results
5.1. State-of-the-art image generation
매우 적은 시간으로, diffusion model의 성능을 처음으로 능가했습니다.
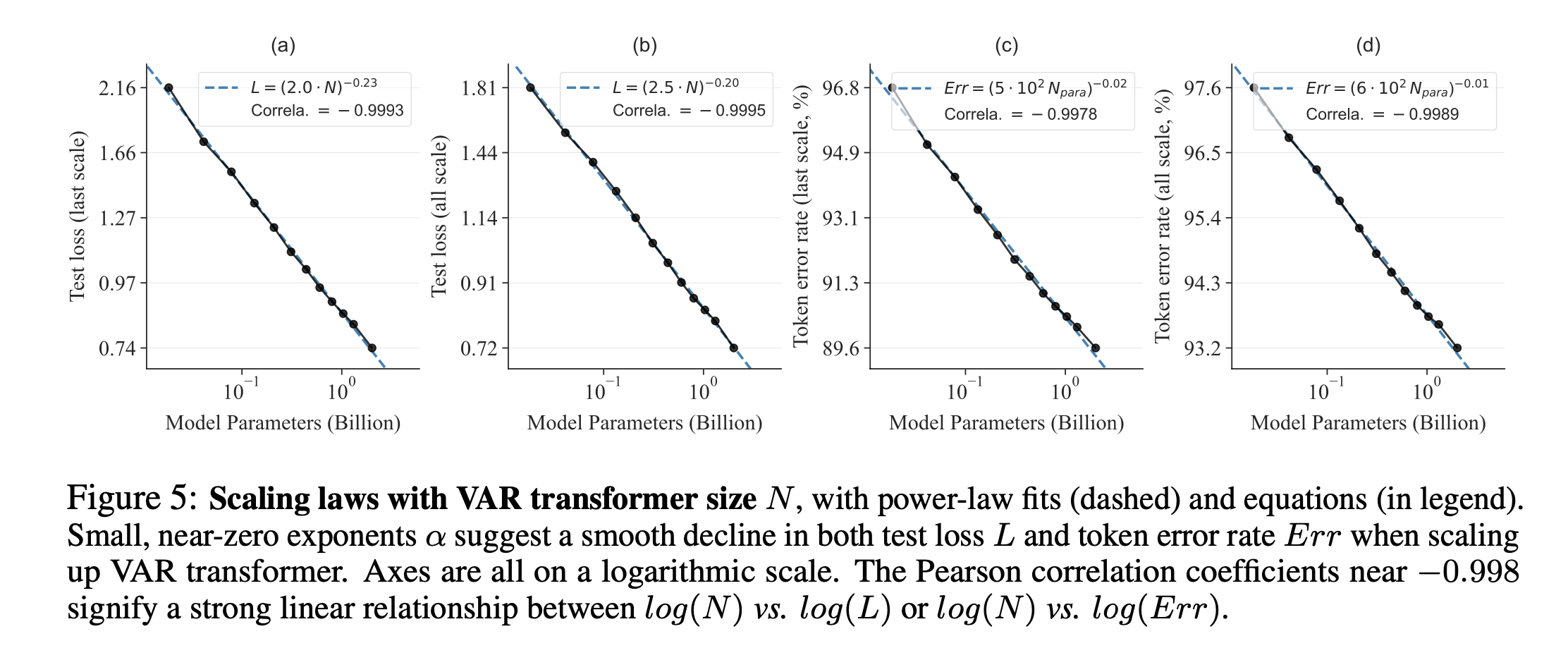
5.2. Power-law scaling laws
scaling law의 특성을 잘 보여줍니다.
5.3. Visualization of scaling effect
오른쪽, 아래로 갈수록 이미지 퀄리티가 확실히 좋아 보이네요.
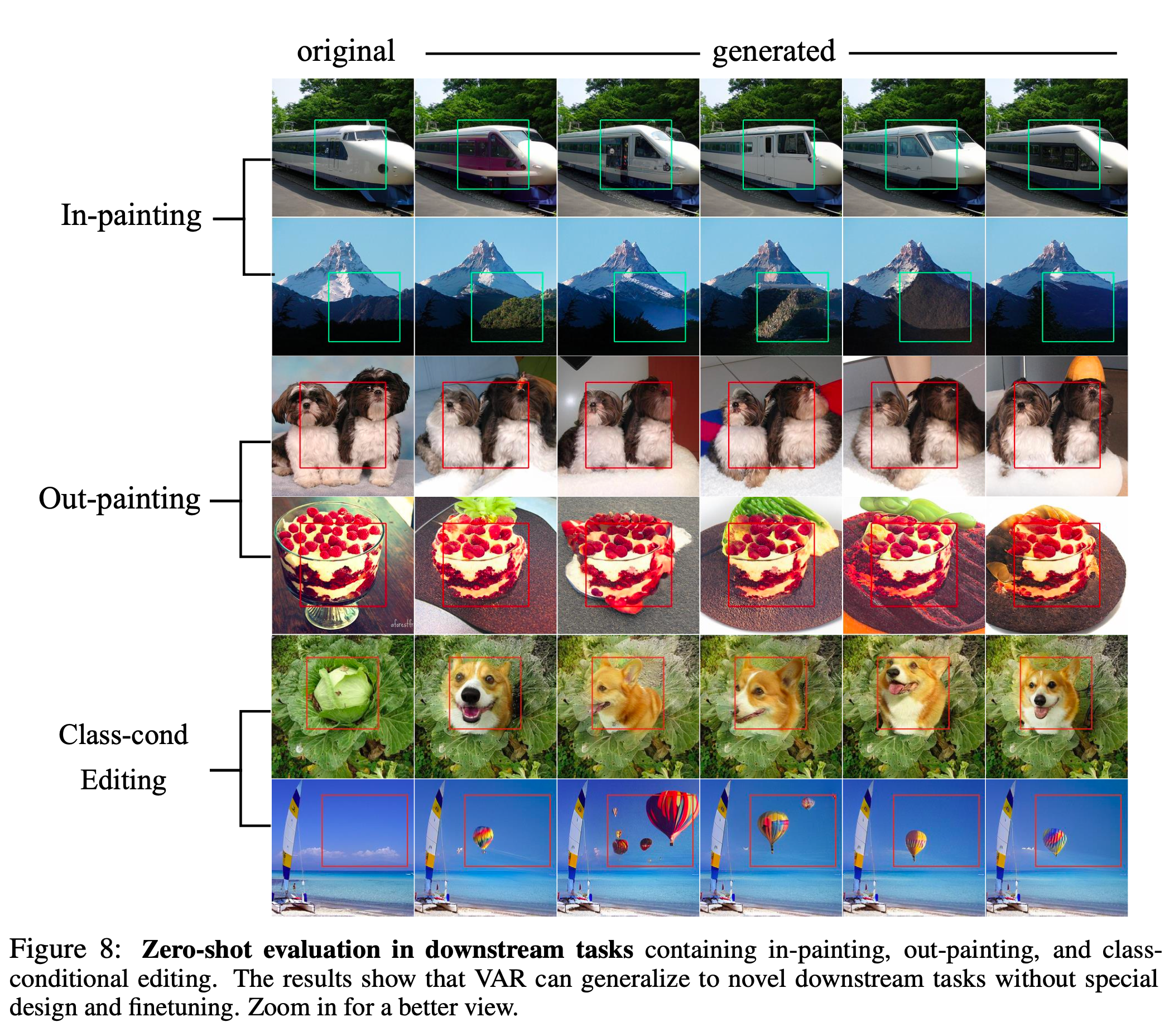
6. Zero-shot task generalization
저자들은 AR기반 LLM의 주요 특성인 Zero-shot task generalization에 대해서도 실험결과를 제시합니다.
zero-shot인데 생각보다 성능이 잘 나오네요…
8. Limitations and Future Work
이번 연구에서 저자들은 새로운 학습 패러다임에 초점을 맞추었으며, VQVAE의 구조나 학습 과정을 그대로 유지했다고 합니다. 저자들의 연구와는 별개로, VQVAE tokenizer의 발전은 AR 생성 모델의 성능을 높이는 방법이 될 것이라 생각된다고 합니다.
Future work으로는, Text-prompt generation으로 확장하는 것이 최우선 목표라고 합니다.
논문 읽는 중에 새로운 paper가 나왔습니다. 다음 포스팅으로…
혹은 Video generation으로 확장해 기존 AR 모델에 비해 훨씬 효율적인 고해상도 비디오 생성이 가능할 것이라 합니다.
9. Conclusion
저자들의 주요 기여를 정리하자면 다음과 같습니다.
- 기존 AR 모델의 문제를 이론적으로 다룹니다.
- 처음으로 AR 방식으로 diffusion 모델의 성능을 능가했습니다.
- VAR 모델로 scaling law, zero-shot 일반화 성능을 보입니다.